Anti-pylon Brits Could Herald New Off-grid Era
Retired film-maker Christopher Hamblin is unmoved at the prospect of a lump-sum payment from developers to compensate him for electricity towers and cables they want to build near his village in the east of England.
“That’s the trouble with these guys — they know the price of everything and the value of nothing,” says the 86-year-old resident of Ardleigh in Essex, a centuries-old settlement surrounded by some of the country’s most recognisable landscapes.
Hamblin and his fellow residents are part of a growing backlash in local communities across Britain against the expansion of power grids as the steps needed to decarbonise the economy start to encroach on them.
In an attempt to counter this resistance Nick Winser, the government’s electricity networks commissioner, has recommended lump-sum payments to households living close to proposed transmission lines. It was one of several measures aimed at cutting in half the 14 years it takes to complete these projects.
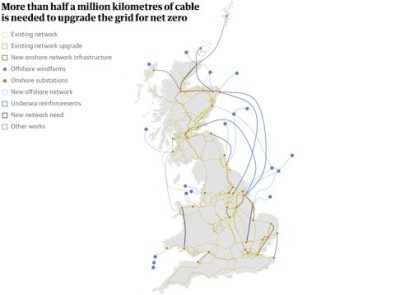
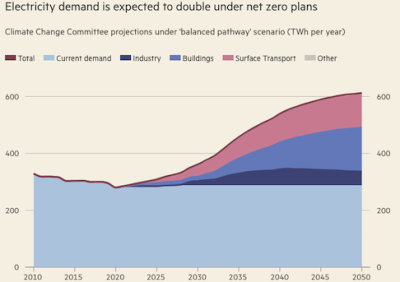
The government wants to decarbonise the electricity sector by 2035, while demand for electricity is expected to double or treble as the economy moves away from fossil fuels under its legally binding target of net zero carbon emissions by 2050. Electric Vehicles and AI data centres have added a crushing new burden.
The offer of cash for pylons (as towers are named in the UK) has not changed the mood in Ardleigh, which is in the path of a new 183km north-south high voltage transmission line that National Grid wants to build through the East Anglian countryside. It would run from Norwich in Norfolk down to Tilbury in Essex and bring in renewable electricity generated from new offshore wind farms.
It is one of several new electricity transmission lines being planned around Britain to move clean electricity often generated in remote coastal locations into more populated areas where it is needed.
The East Anglia plan mainly involves cables carried on 50m-tall pylons dotted across the countryside, including around Ardleigh, which sits on the edge of the protected countryside of Dedham Vale, made famous in the 19th-century masterpieces by local artist John Constable.
The reason for the opposition varies, ranging from blighting the landscape to the impact on farmers or health, but most opponents would rather see the power lines replaced by undersea cables running from the wind farms most of the way down to Tilbury.
“Every single house within that location — we will be in a cage of electricity pylons,” says Chris Whitfield, chair of Ardleigh parish council, pointing out part of the proposed route on a map.
Campaigners are well-organised, learning from other groups across the country, and are prepared to resort to legal action.
Local farm owner Charles Tritton suggested the anger is such that it could hurt the Tory party electorally. “The whole of East Anglia is pretty Conservative,” he said. “Add one or two per cent [swing vote] due to this …