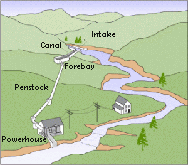
A Typical MH set-up on a river. If you have a stream, you have a renewable, natural source of energy that, if done right, can have little to no impact on the environment around you. Using water as a power source goes back to ancient times. Roman was known to power their empire on it. There is abundant supply of streams and rivers that criss cross the US making micro-hydro power feasible. That is especially true in remote wooded areas where other natural energy, such as solar or wind, would be harder to integrate into the existing environment.
A micro-hydro power system needs a sufficient amount of falling water to be available in order to be feasible. Mountainous and hilly sites are best suited for this type of renewable energy. To figure out the amount of power that is possible from your water source you need to know the head and flow of your stream. The head is the vertical distance of the falling water. While the flow is the speed the water flows at.
A micro-hydro power site usually falls into either a low or high head category. A higher head is better due to needing less water to produce energy as well as the equipment being cheaper than those with a low head. A change in elevation that is less then 10ft (3 meters) is categorized as low head. Anything with a vertical drop less than 2ft (.6 meters) will make a micro-hydro power system not possible. Though if you have as little as 13” of water depth you are able to utilize a submersible turbine, which was originally designed to power scientific instruments being towed behind exploration ships.
There is both a gross and net head that needs to be calculated. The gross head is the vertical distance between where the water enters the penstock, pipes that convey the water under pressure, to where the water exits the turbine. You calculate your net head by subtracting the friction that is caused by the piping and the turbine itself.
While the best way to get an accurate gross head is to have a professional survey of your desired site, you can do a rough estimate yourself. You can use the hose-tube method by taking stream-depth measurements across the width of the water supply you intend to use. Once you know where you intend to place the beginning of the penstock and the turbine you can follow the direction below.
The Hose-Tube Method is done by:
- Make sure you have all supplies needed: Someone to help, 20ft to 30ft (6 to 9 meters) small diameter garden hose, Funnel, Measuring tape or yardstick
- Stretch the hose down the water channel from desired entrance to the penstock (usually the highest elevation)
- One person place the funnel into the hose upstream as close to the surface as possible
- At the downstream position
…












