
Now Baby Boomers are retiring, they are demanding ethical retirement communities to match their self-image.…

A breakdown of the precise costs of self-building an off-grid, sraw bale, turf roofed house.…
Green or natural landscaping ,also known as native gardening , is when you use indigenous plants in your residential or commercial landscaped gardens. These plants can include local ones such as grasses, ground-cover, wildflowers, shrubs, and trees, as well as using boulders, rocks and locally found material to border theses plantings. Making the landscaped area and the surrounding natural environment blend seamlessly is an important aspect of green landscaping.
Before making the move to change your landscaping to a greener design, you should look into changing your current practices of your existing landscape. Look for ways to reduce your use of power tools. Use mulch, sometimes available from local landfills, to conserve you water needed for your plantings. Making a compost pile to process organic waste and reuse as fertilizer in your gardens. Use natural enemies instead of pesticides to rid your plants of insects, see the EPAs’ integrated pest management for more information.
Now before running to your local nursery or garden store for local plants to use take the time to actually asses your property and the needs you have for it. how much sun and shade does it get and where. What is your soils type(s) and where is your drainage, or do you need more/less drainage. Make a rough plot map that shows your homes’ location including doors, walkways, patios, driveways, etc. Make note of neighbor concerns such as views you wish to keep or cover, noise reduction, privacy issues, etc. Make sure buried utilities are noted, most communities have a service to help with that, as well as overhead lines. Plants that you wish to keep should also be marked and their full height, and known characteristics and needs. Don’t forget to mark your directions of , south, east, and west as well as slopes and their direction and degree.
Once your map is complete now think of what use(s) you want from your land. Do you have children and wish to incorporate a play area or pool, have dogs that need a run, want to grow some or all of your own food, need to store a boat or RV, need additional buffers for privacy, noise or wind, and any other concerns or desires you can think of.
Now you need to research your local environment. What plants are native, which plants work well together, what plants meet your needs. Going to local parks and nature centers and walking through them will give you ideas of your likes and dislikes. Local park service may even have clinics or talks to help you. Use the internet and research your zone. The EPA website has dedicated sections to each geographic zone and how to green landscape there.
Time for putting it all together on you map and then start buying your new plants. Once your plan is completed go for it. All this work will pay …
Some problems with traditional lanscaping are water pollution, air pollution, noisew pollution, consumption of our natural resources, produces solid waste, harmful to health and safety, declining biodeiversity, flooding, and to top it off it’s labor and cost intensive.
Homeowners over-apply pesticides and fertilizers often more than that of farmers. Additionaly people dump excess pesticides on the ground, in their drains, and/or in their trash rather than taking them to hazardous waste collection sites. Plus since turf has such a shallow roots and is a bad stabilizer for stream banks, so that heavy rains can result in bank erosion and stream silation. Added to that is the tens of millions of gallons of gasoline that are spilled each year while refueling garden equipment. Water pollution is increased with traditional gardening by:
Air pollution is contributed to by the operating and refueling of landscape equipment, vehiclesEmissions from landscape equipment (mowers, blowers, trimmers, etc.). These are often greater than that of a car per hour of operation. The most polluting are small gasoline-powered engines.
Noise Pollution is added to by the operation of the power equipment and vehicles need to maintain traditional lanscaping. How often have you been outside on a blissfully warm day only to have it ruined by a neighbor mowing their lawn? Some actual lanscaping equipment can actually lead to hearing impaiement.
Using up our limited supply of natural resources to have curb appeal is not the wisest action we could be doing. 30% of our water consumption in the urban areas of the eastern United States is to water lawns. Additional resources that are being consumed to improve our yards and gardens in traditional methods are:
Adding grass clippings and leaves to our everday trash collections. Almost 1/5 of all solid waste collected by municipals are yard waste and organic waste that could be composted by homeowners. Though some is then composted by the municipalities, most ends up in landfills that are quickly reaching capacity.
On top of those concerns is that of health and safety to ourselves. The repeated exposure to chemical pesticides nad accidents that can occur from the use of power tools and equipment. By gardeners over using or not following directions of pesticides they are putting themselves, their families, neighbors, and even animals in increased health risk. Adding to that is that nearly half of all households have stored pesticides within reach of children. 230,000 people every year are treated in hospital emergency rooms for injuries related to lawn and garden tools.
Non-native plants can “escape” from gardens …

“Farewell my Subaru” is the story of bumbling radio presenter who tries to take his life off-grid …
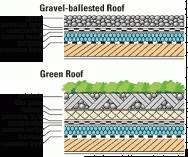
 An alternative to your traditional roofing materials is a “green roof”, or a rooftop garden. The surface temperature of a vegetated roof is able to be cooler than the surrounding air temperatures unlike that of a traditional roof surface can be up-to 90°F (50°C) hotter. You can not only improve your energy efficiency but add more greenery to your environment, take a look at the green roof on City Hall of Atlanta Georgia.
An alternative to your traditional roofing materials is a “green roof”, or a rooftop garden. The surface temperature of a vegetated roof is able to be cooler than the surrounding air temperatures unlike that of a traditional roof surface can be up-to 90°F (50°C) hotter. You can not only improve your energy efficiency but add more greenery to your environment, take a look at the green roof on City Hall of Atlanta Georgia.
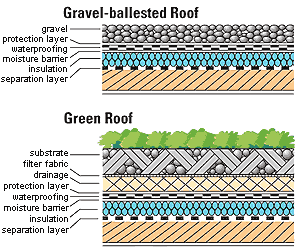
Green roofs are defines as having vegetation and soil, or another growing medium, that is planted over a waterproof material. Some roofs may also include the additional layers of a root barrier, drainage, and/or irrigation system.
The nice thing about green roofs is that it can be incorporated into many different types of buildings, such as residences, offices, industrial facilities, and other commercial buildings. they are widely used in Europe for their great storm water management, energy saving ability, and their beauty.
This attractive roofing option can reduce urban heat islands with their provided shade and the release of water from the plants to the surrounding air. Additional benefits include:
 Green roofs can help mitigate storm water runoff. As buildings, pavements, roads, and other impermeable surfaces replace open fields and vegetation, this roofing option can play an important role in storm water management. During storms they can absorb much of the water that would otherwise run off. It is estimated that 3-5 inches of soil or another growing medium can absorb 75% of a rain event of 1/2 inch or less.
Green roofs can help mitigate storm water runoff. As buildings, pavements, roads, and other impermeable surfaces replace open fields and vegetation, this roofing option can play an important role in storm water management. During storms they can absorb much of the water that would otherwise run off. It is estimated that 3-5 inches of soil or another growing medium can absorb 75% of a rain event of 1/2 inch or less.
While absorbing this rainwater it also filters the pollution out of it. This is done by the bacteria and fungi in the root system, utilizing the natural filtering process. This results in nitrogen and phosphorous being broken down and detoxified. Over time this process will only increase as the plants and root system mature on the roof.
Green roofs are available in two types, Intensive Green Roof and Extensive Green Roof.
The Intensive Green Roof is characterized by:
The Extensive Green Roof is …
In most old homes windows are one of the largest sources of heating during the winter do to their low insulating ability combined with high air leakage. During the summer they are also a major source of additional unwanted heat. This results in windows being typically net energy loser, that can be responsible for 25% to 50% of the energy needed to heat and cool your home. There is hope in the form of new and improved windows and giving proper consideration for the actual placement of them can result in making them a positive in helping to maintain comfortable home environment.
If you are considering replacing or adding new windows there are some basic factors to consider. They can include glazing type, orientation, shading, total area of windows and their insulation values, plus the actual installation method. You can access the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) directory of windows and doors by clicking here. They are a non-profit organization with a directory of over 1.6 million products and 500 manufactures that have been rated and tested. They provide ratings that indicate the whole window U-value. This not only includes the insulating of the glazing and frame, but also low e-glazing, gas fillings, tinting and films. The information includes product types, number of glazing layers, presence of low-e and value, spacer type, and gap fill and spacing.
Some other considerations besides that of the actual windows chosen are air leakage and placement/orientation. Air leakage cannot only occur around but through your windows and can have serious effect on your energy efficiency and comfort level. Weatherstripping and caulking can be done around existing windows to improve the air tight seal desired. New windows are routinely checked for air leaks between their frame and sash. Leakage rates between .01 and .06 cfm/ft of perimeter are considered better windows. Windows types with lower rates of air leakage are hopper, casement, and awning then double hung or sliders. Check information provided by the manufacturer for the information on air leakage.
A design considerations that can provide a net energy gain for your windows is to allow the sun light to enter the windows during the winter and block it during the summer. As the sun is lower in the winter then in the summer placement and depth of windows along with awnings can have a huge impact on your heating and cooling. You want to reduce the area of windows on the east and west sides to help avoid summer heat gain. Use overhangs, awnings or vegetation, such as trees, to shade your windows. Limit your use of skylights as in summer they add heat while in winter not enough.…

World’s press taken in by massive launch party for Arab eco-city. In fact its self-professed aim is to allow more oil to be drilled, while the eco-city itself is merely a dormitory town for nearby Abu Dhabi.…
Earthships are earth-sheltered autonomous buildings made of tires rammed with earth, which are usually arranged in “U” or horseshoe shaped modules. Each tire is rammed full of earth manually using a sledge hammer. Windows on the sunny side admit light and heat. The open end of the “U” shaped structure faces South in the northern hemisphere, and North in the southern hemisphere, so that the house will catch maximum sunlight in the colder months. An Earthship is designed to interface with its environment wherever possible and create its own utilities.
Internal, non-load-bearing walls are often made of a “honey comb” of recycled cans separated by concrete. The walls are then usually thickly plastered, using the pull-tabs on the cans as a lath to hold the adobe and stucco. This is known as a tin can wall. The roof of an Earthship is heavily insulated.
The Earthship, as it exists today, began to take shape in the 1970s. Mike Reynolds, founder of Earthship Biotecture, a company that specializes in designing and building Earthships, wanted to create a home that would do three things. First, it would be sustainable. It would use material indigenous to the entire planet as well as reuse materials wherever possible. Second, his homes would generate their own utilities and be independent from the “grid” so they would be less susceptible to natural disasters and free from the electrical and water grids that Reynolds considered ugly. Finally, it would be available. He wanted to create a home that the average person with no specialized construction skills would be able to create.
Eventually, his vision took the form of the common U-shaped earth-rammed tire home seen today. However, as a concept, the Earthship is not limited to earth-rammed tires. Any dense material with a potential for thermal mass, such as concrete, adobe, or stone can be used to create an Earthship. However, the earth-rammed tire version of the Earthship is now the most common for several reasons, and is usually the only structure referred to as “Earthship”.
Unlike other materials, rammed-earth tires are more accessible to the average person. Scrap tires are indigenous to all parts of the world and easy to come by; there are an estimated 2 billion tires throughout the United States. According to the Scrap Tire Management Council, as many as 253 million scrap tires are generated each year in the United States and of those 253 million tires only 53% are reclaimed by the scrap tire market. In addition to the availability of scrap tires, the method by which they are produced, the ramming of the earth, is simple and affordable.
The earth rammed tires of an Earthship are usually assembled by teams of two people working together as part of a larger construction team. One member of the two person team shovels dirt, which usually comes from the building site, placing it into …